All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
- – Geologists And Geophysicists in Piesse Brook ...
- – 5 Surface Geophysics in Leeming WA 2023
- – Gravity Geophysical Survey Method in Kewdale...
- – Geophysicist - Jobs And Skills Wa in Eden H...
- – Geophysical Survey - Archaeological Researc...
- – Geophysical Services in Balga Western Aust...
- – Bs In Physics: Geophysics in Cardup Aus 2020
Geologists And Geophysicists in Piesse Brook WA 2020
doi:10. 1556/AGeod. 45.2010. 2.9. S2CID 122239663. Temple 2006, pp. 162166 Russo, Lucio (2004 ). Berlin: Springer. p. 273277. Temple 2006, pp. 177181 Newton 1999 Area 3 American Geophysical Union (2011 ). "Our Science". About AGU. Recovered 30 September 2011. "About IUGG". 2011. Recovered 30 September 2011. "AGUs Cryosphere Focus Group". 2011. Archived from the original on 16 November 2011.
Bozorgnia, Yousef; Bertero, Vitelmo V. (2004 ). Earthquake Engineering: From Engineering Seismology to Performance-Based Engineering. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-1439-1. Chemin, Jean-Yves; Desjardins, Benoit; Gallagher, Isabelle; Grenier, Emmanuel (2006 ). Mathematical geophysics: an introduction to rotating fluids and the Navier-Stokes formulas. Oxford lecture series in mathematics and its applications. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-857133-X.
( 2001 ). Dynamic Earth: Plates, Plumes and Mantle Convection. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-59067-1. Dewey, James; Byerly, Perry (1969 ). "The Early History of Seismometry (to 1900)". Publication of the Seismological Society of America. 59 (1 ): 183227. Archived from the original on 23 November 2011. Defense Mapping Agency (1984 ). (Technical report).
5 Surface Geophysics in Leeming WA 2023
TR 80-003. Obtained 30 September 2011. Eratosthenes (2010 ). Eratosthenes' "Geography". Pieces gathered and equated, with commentary and additional product by Duane W. Roller. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-14267-8. Fowler, C.M.R. (2005 ). (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-89307-0. "GRACE: Gravity Healing and Climate Experiment". University of Texas at Austin For Area Research Study.
Obtained 30 September 2011. Obtained 30 September 2011.:10.
Gravity Geophysical Survey Method in Kewdale Western Australia 2022
Lowrie, William (2004 ). Merrill, Ronald T.; Mc, Elhinny, Michael W.; Mc, Fadden, Phillip L. (1998 ). International Geophysics Series.
They also research modifications in its resources to offer assistance in conference human needs, such as for water, and to predict geological risks and dangers. Geoscientists use a variety of tools in their work. In the field, they may utilize a hammer and chisel to collect rock samples or ground-penetrating radar equipment to look for minerals.
They likewise might use remote sensing equipment to gather data, in addition to geographic info systems (GIS) and modeling software to examine the data collected. Geoscientists might monitor the work of specialists and coordinate work with other scientists, both in the field and in the lab. As geological difficulties increase, geoscientists might decide to work as generalists.
Geophysicist - Jobs And Skills Wa in Eden Hill Australia 2023
The following are examples of types of geoscientists: geologists study how consequences of human activity, such as contamination and waste management, impact the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They likewise may work to solve issues associated with natural dangers, such as flooding and disintegration. study the materials, procedures, and history of the Earth.
There are subgroups of geologists too, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and composition of minerals. study the motion and flow of ocean waters; the physical and chemical homes of the oceans; and the methods these homes affect coastal areas, climate, and weather.
They likewise research study changes in its resources to offer assistance in conference human needs, such as for water, and to forecast geological threats and risks. Geoscientists utilize a range of tools in their work. In the field, they may utilize a hammer and sculpt to gather rock samples or ground-penetrating radar equipment to search for minerals.
Geophysical Survey - Archaeological Research in Kingsley Australia 2021
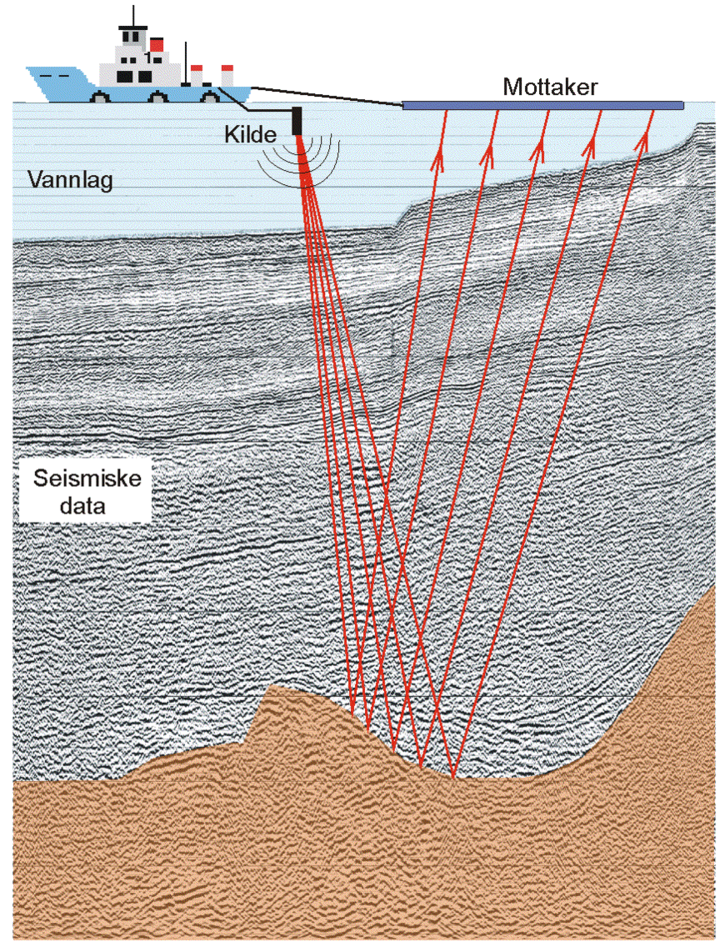
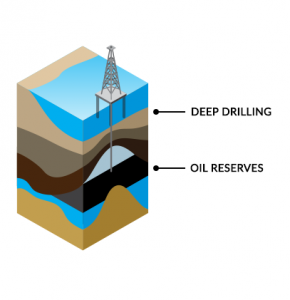
They likewise might utilize remote picking up equipment to gather information, along with geographic information systems (GIS) and modeling software to analyze the information collected. Geoscientists might monitor the work of professionals and coordinate deal with other researchers, both in the field and in the laboratory. As geological difficulties increase, geoscientists may choose to work as generalists.
The following are examples of types of geoscientists: geologists study how consequences of human activity, such as pollution and waste management, impact the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They also may work to solve problems related to natural risks, such as flooding and disintegration. study the products, processes, and history of the Earth.
There are subgroups of geologists too, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and structure of minerals. study the motion and blood circulation of ocean waters; the physical and chemical properties of the oceans; and the methods these residential or commercial properties affect seaside locations, climate, and weather condition.
Geophysical Services in Balga Western Australia 2022
They also research study changes in its resources to supply guidance in meeting human needs, such as for water, and to forecast geological risks and dangers. Geoscientists utilize a range of tools in their work. In the field, they may utilize a hammer and chisel to gather rock samples or ground-penetrating radar equipment to look for minerals.
They also might use remote picking up equipment to collect data, as well as geographical details systems (GIS) and modeling software to analyze the information gathered. Geoscientists may supervise the work of service technicians and coordinate work with other researchers, both in the field and in the laboratory. As geological challenges increase, geoscientists may choose to work as generalists.
The following are examples of types of geoscientists: geologists study how effects of human activity, such as contamination and waste management, affect the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They also might work to resolve issues associated with natural threats, such as flooding and disintegration. study the materials, processes, and history of the Earth.
Bs In Physics: Geophysics in Cardup Aus 2020
There are subgroups of geologists also, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and composition of minerals. study the motion and circulation of ocean waters; the physical and chemical residential or commercial properties of the oceans; and the methods these homes affect seaside locations, environment, and weather condition.
Table of Contents
- – Geologists And Geophysicists in Piesse Brook ...
- – 5 Surface Geophysics in Leeming WA 2023
- – Gravity Geophysical Survey Method in Kewdale...
- – Geophysicist - Jobs And Skills Wa in Eden H...
- – Geophysical Survey - Archaeological Researc...
- – Geophysical Services in Balga Western Aust...
- – Bs In Physics: Geophysics in Cardup Aus 2020
Latest Posts
Geoscientist - College Of Science in St James Aus 2021
What Is A Seismic Survey? in Straffon Oz 2021
What Are Geological, Geochemical, in Hovea WA 2022
More
Latest Posts
Geoscientist - College Of Science in St James Aus 2021
What Is A Seismic Survey? in Straffon Oz 2021
What Are Geological, Geochemical, in Hovea WA 2022