All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
- – Consumer Guide To Geological And Geophysical ...
- – 5 Surface Geophysics in Bedford Western Aust...
- – Marine Geophysical Surveying - in Burswood W...
- – Job Profiles : Geophysicist Physics in Muns...
- – What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Oakford Aus...
- – Geophysicist in Two Rocks WA 2020
- – What Do Geoscientists And Hydrologists Do?...
Consumer Guide To Geological And Geophysical Services ... in Leeming Aus 2023
doi:10. 1556/AGeod. 45.2010. 2.9. S2CID 122239663. Temple 2006, pp. 162166 Russo, Lucio (2004 ). Berlin: Springer. p. 273277. Temple 2006, pp. 177181 Newton 1999 Area 3 American Geophysical Union (2011 ). "Our Science". About AGU. Retrieved 30 September 2011. "About IUGG". 2011. Obtained 30 September 2011. "AGUs Cryosphere Focus Group". 2011. Archived from the initial on 16 November 2011.
Bozorgnia, Yousef; Bertero, Vitelmo V. (2004 ). Earthquake Engineering: From Engineering Seismology to Performance-Based Engineering. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-1439-1. Chemin, Jean-Yves; Desjardins, Benoit; Gallagher, Isabelle; Grenier, Emmanuel (2006 ). Mathematical geophysics: an introduction to rotating fluids and the Navier-Stokes equations. Oxford lecture series in mathematics and its applications. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-857133-X.
Publication of the Seismological Society of America. 59 (1 ): 183227. Defense Mapping Company (1984 ).
5 Surface Geophysics in Bedford Western Australia 2021
TR 80-003. Obtained 30 September 2011. Eratosthenes (2010 ). Eratosthenes' "Location". Fragments gathered and equated, with commentary and extra product by Duane W. Roller. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-14267-8. Fowler, C.M.R. (2005 ). (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-89307-0. "GRACE: Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment". University of Texas at Austin Center for Space Research Study.
Retrieved 30 September 2011. Hardy, Shaun J.; Goodman, Roy E. (2005 ). "Web resources in the history of geophysics". American Geophysical Union. Archived from the initial on 27 April 2013. Retrieved 30 September 2011. Harrison, R. G.; Carslaw, K. S. (2003 ). "Ion-aerosol-cloud procedures in the lower atmosphere". 41 (3 ): 1012. Bibcode:2003 Rv, Geo..41.
doi:10. 1029/2002RG000114. S2CID 123305218. Kivelson, Margaret G.; Russell, Christopher T. (1995 ). Intro to Space Physics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-45714-9. Lanzerotti, Louis J.; Gregori, Giovanni P. (1986 ). "Telluric currents: the natural environment and interactions with man-made systems". In Geophysics Study Committee; Geophysics Research Online Forum; Commission on Physical Sciences, Mathematics and Resources; National Research Study Council (eds.).
Marine Geophysical Surveying - in Burswood WA 2022
The Earth's Electrical Environment. National Academy Press. pp. 232258. ISBN 0-309-03680-1. Lowrie, William (2004 ). Fundamentals of Geophysics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-46164-2. Merrill, Ronald T.; Mc, Elhinny, Michael W.; Mc, Fadden, Phillip L. (1998 ). The Electromagnetic field of the Earth: Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle. International Geophysics Series.
They likewise research study modifications in its resources to offer guidance in conference human demands, such as for water, and to forecast geological threats and hazards. Geoscientists use a variety of tools in their work. In the field, they might use a hammer and chisel to collect rock samples or ground-penetrating radar equipment to look for minerals.
They also may use remote noticing equipment to gather data, along with geographical info systems (GIS) and modeling software to analyze the information gathered. Geoscientists may supervise the work of specialists and coordinate deal with other researchers, both in the field and in the lab. As geological obstacles increase, geoscientists may decide to work as generalists.
Job Profiles : Geophysicist Physics in Munster Oz 2023
The following are examples of types of geoscientists: geologists study how effects of human activity, such as contamination and waste management, affect the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They likewise may work to fix issues connected with natural risks, such as flooding and disintegration. study the materials, processes, and history of the Earth.
There are subgroups of geologists as well, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and structure of minerals. study the motion and flow of ocean waters; the physical and chemical homes of the oceans; and the ways these residential or commercial properties affect coastal areas, climate, and weather.
They likewise research modifications in its resources to supply assistance in conference human needs, such as for water, and to predict geological risks and risks. Geoscientists use a range of tools in their work. In the field, they may utilize a hammer and chisel to collect rock samples or ground-penetrating radar devices to search for minerals.
What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Oakford Australia 2020
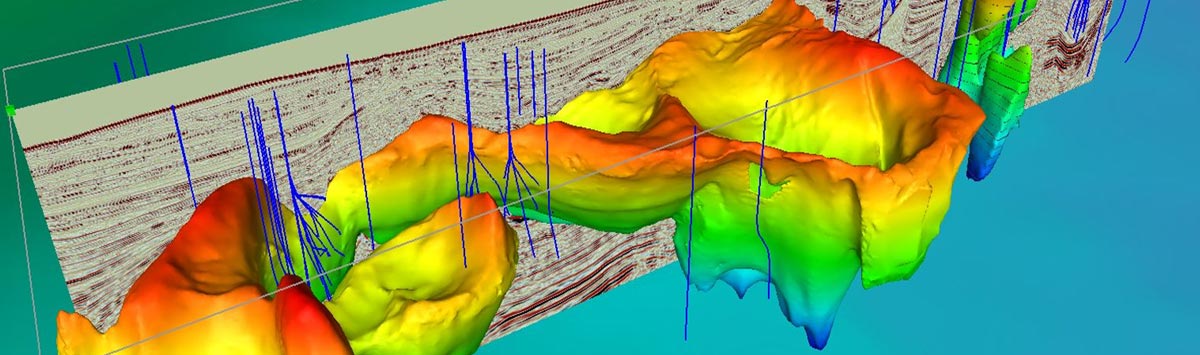

They also may use remote picking up equipment to gather data, in addition to geographic info systems (GIS) and modeling software application to analyze the information gathered. Geoscientists may monitor the work of service technicians and coordinate deal with other scientists, both in the field and in the lab. As geological obstacles increase, geoscientists may choose to work as generalists.
The following are examples of kinds of geoscientists: geologists study how consequences of human activity, such as contamination and waste management, impact the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They likewise might work to solve problems related to natural hazards, such as flooding and disintegration. study the products, processes, and history of the Earth.
There are subgroups of geologists too, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and composition of minerals. study the motion and flow of ocean waters; the physical and chemical properties of the oceans; and the ways these properties affect coastal areas, environment, and weather condition.
Geophysicist in Two Rocks WA 2020
They likewise research study changes in its resources to supply assistance in conference human demands, such as for water, and to forecast geological threats and threats. Geoscientists use a range of tools in their work. In the field, they may utilize a hammer and sculpt to collect rock samples or ground-penetrating radar equipment to search for minerals.
They likewise may use remote sensing equipment to gather information, along with geographical info systems (GIS) and modeling software to analyze the information collected. Geoscientists might monitor the work of service technicians and coordinate deal with other researchers, both in the field and in the lab. As geological difficulties increase, geoscientists may choose to work as generalists.
The following are examples of types of geoscientists: geologists study how effects of human activity, such as contamination and waste management, impact the quality of the Earth's air, soil, and water. They likewise may work to fix problems related to natural hazards, such as flooding and disintegration. study the materials, processes, and history of the Earth.
What Do Geoscientists And Hydrologists Do? in Brookdale Oz 2023
There are subgroups of geologists as well, such as stratigraphers, who study stratified rock, and mineralogists, who study the structure and composition of minerals. study the motion and circulation of ocean waters; the physical and chemical homes of the oceans; and the ways these residential or commercial properties affect seaside areas, climate, and weather.
Table of Contents
- – Consumer Guide To Geological And Geophysical ...
- – 5 Surface Geophysics in Bedford Western Aust...
- – Marine Geophysical Surveying - in Burswood W...
- – Job Profiles : Geophysicist Physics in Muns...
- – What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Oakford Aus...
- – Geophysicist in Two Rocks WA 2020
- – What Do Geoscientists And Hydrologists Do?...
Latest Posts
Geoscientist - College Of Science in St James Aus 2021
What Is A Seismic Survey? in Straffon Oz 2021
What Are Geological, Geochemical, in Hovea WA 2022
More
Latest Posts
Geoscientist - College Of Science in St James Aus 2021
What Is A Seismic Survey? in Straffon Oz 2021
What Are Geological, Geochemical, in Hovea WA 2022